Lecture XI - Managing
Capacity and Demand 25.10.11
Discussion of case
- difference between season and cycle → the different in time period
- increasing trend or not → use line of regression
- might be seasonal plus increasing trend
exponential smoothing →
deseasonalise
bottom line projection →
smoothing with current data
- forecasted demand for next few periods
- supply side known → demand have to vary (depends on services, hot to manage supply and demand)
- limited/ impossible capacity increase (high fixed costs)
- perishable services capacity
- demand fluctuations, difficult to predict
- variability in service time
- services are rarely uniform and single
Two basic approaches:
- adjust level of capacity to meet demand
- manage level of demand
Flexing capacity to match
demand
Case p. 380 → case:
Gateway International Airport
LP problem … use LP
model, different hours of shift
Excel calculation of a
given system... define time shifts and use across all these days the
number of people in the shift while considering daily variation
Managing Demand (capacity
known)
- pricing, promotion, marketing strategy etc..
- design multi – stage production process → e.g. multiple counters at hospital
- managing queues and waiting times → queuing system* unoccupied times feels longer than occupied time* uncertain waits are longer than known finite waits* unexplained waits much longer than explained* pre process wait feel longer than process wait* anxiety makes wait seem longer
Yield Management
- ability to segment markets
- overbooking → compensate overbooked customer
- e.g. upgrade users to AC3 to make space and sell AC2 seats in train
- balance past benefits and minimize loss/ costs
- PURPOSE of yield Management: How much should I overbook (in $)?
- e.g. Hotel overbooking problem... chose number of possible over bookings when the cost is minimum
Aggregate planning in
services
Lecture X - Forecasting 18.10.11
Two case presentations
“to err is human, to
recover, divine” close loops
to err = sich irren
Nominal Group Technique
(NGT)
- a face to face Delphi method, allowing group discussion
- quicker than Delphi
Delphi method
The Delphi method is a
structured communication technique, originally developed as a
systematic, interactive forecastingmethod which relies on a panel of
experts. In the standard version, the experts answer questionnaires
in two or more rounds. After each round, a facilitator provides an
anonymous summary of the experts’ forecasts from the previous round
as well as the reasons they provided for their judgments. Thus,
experts are encouraged to revise their earlier answers in light of
the replies of other members of their panel. It is believed that
during this process the range of the answers will decrease and the
group will converge towards the "correct" answer. Finally,
the process is stopped after a pre-defined stop criterion (e.g.
number of rounds, achievement of consensus, stability of results) and
the mean or median scores of the final rounds determine the results.
Delphi is based on the
principle that forecasts (or decisions) from a structured group of
individuals are more accurate than those from unstructured groups.
This has been indicated with the term "collective intelligence".
The technique can also be adapted for use in face-to-face meetings,
and is then called mini-Delphi or Estimate-Talk-Estimate (ETE).
Delphi has been widely used for business forecasting and has certain
advantages over another structured forecasting approach, prediction
markets. ---wiki---
Time series components
- trend
- cyclical
- seasonal
- random
Exponential smoothing
method (averaging)
- form of weighted moving average (weights decline exponentially, most recent data weighted more)
- requires smoothing constant (alpha), which ranges from 0 to 1, subjectively chosen
- involves life record keeping of past data; to recognize the pattern
Actual Forecasted
only when huge fluctuation
need
at longer time frame (use
trend)
→ Premise – The most
recent observations is normally a better to predict the next
observation than are older observations (more weight to the more
recent time periods when forecasting)
Choosing alpha
seek to minimize the mean
absolute deviation (MAD)
IF: forecast error =
demand – forecast
Then: MAD = Sum |forecast
errors|
Clark Wright Algorithm
Lecture IX - Service
Quality Continued 11.10.11
Designing a walk
through audit
Quality Control check
sheet (p.135) to ask customers, employees and stakeholders
GAP model may be used to
identify gaps “happy employees = happy customers”
“benefits
without costs is very good, benefits with additional costs is very
bad”
- it provides a framework for translating customer satisfaction into identifiable and measurable content
- What do the customer want/ need? → everyone has different view/ not possible to satisfy all needs = selecting most valued ones
- what do I want to become? Vision and mission in mind to make the right selection/ prioritize
→ relationship matrix
(Schliemann und Systemanalyse)
creation of points and
figuring out their interrelation. Possible to break down in smaller
units to become more specific.
A way to get insights into
competitors is to hire a former employee who worked at the competitor
Taguchi Techniques
- Quality loss concept
- the more away from the target, the more compensation for customer (due to customer loss)
Poka-Yoke applied to
services
Service Guarantee
- unconditional – the more inclined conditions, the less attractive for client
Service Recovery
What is the purpose of the
case? Should I have a service guarantee or not? (e.g. might increase
market share, does company require a service guarantee?)
- a poor company should not give service guarantee → too difficult and demand for its system
- a company that is able to manage income parameters and is somewhere in between (with potential to improve) can opt for a service guarantee (understanding risk)
Lecture VIII – Service
Quality 04.10.11
Lambda (What is the Lambda
that you are taking?) its impact...
Why is the model divided
this way?
When the customer has a
choice (in developed countries), but not in undeveloped countries.
Definition of quality
- product based - presence/ absence of an attribute
- user based – ability to meet the user's expectations
Quality = Service quality
+ product quality + price
Eight dimensions/
categories of product quality
- performance
- features
- reliability
- conformance
- durability
- serviceability
- aesthetics
- perceived quality
Service quality attributes
- accessible
- empathy
- communication
- understanding
- tangibles (smalls things that show I care four you)
- reliability (opening hours, Internet reservation)
- responsiveness
- competence
- credibility
- courtesy (willingness to listen)
- security
Customer satisfaction is
influenced by nature of service expectation
Dissatisfaction / Delight
The Quality Gap model
(Gaps 1 to Gap 5) How can I detect them and improve them?
Process Model for
continuous Measurement and improvement of service quality
→ customer feedback on
operational stages!
Measuring service quality
with SERVQUAL (page 132 in book)
- assessing whether I give what I intended to give (limit questionnaire to 1 – 2 pages)
- to get unbiased opinion of service
- is a multiple item scale for measuring five dimensions of service quality (PRAET). It is a two part instrument with initial sections to record customers expectations from a class of service and the second section to record customers perception of a particular service firm
- score of the quality by differences of items→ customer mainly value reliability, assurance, responsiveness, empathy
“What can I do? If I
complain replacement will be same quality!”
Companies should show more
concern about “No action customers” .
Walk-through-Audit
(WtA)
- run through entire process and get feedback from employers, customers, and designed
- use all the senses to get customers' impression
- service managers lose sensitivity due to familiarity
- need detailed service audit from a customer's perspective
HW:
read example page 135, and
145 – 147
Case about “Profitable
art of service recovery”
Lecture VII - Service
Facility Location part 2 30.09.11
- Load Distance Technique (Euclidian Metric)
- Location Break Even Analysis
- Huff Retail Location Model (may calculate market share)
Multiply Facility
Locations
- e.g. distance – How many more locations are needed to cover an area?
Case of Athol Furniture
using Huff model (where located, how big)
The supporting facility
(Service facility layout)
How
to use a given space and design
Servicescapes
- physical environment of supporting facility that influences both customers and employees
- ambient conditions
- spacial layout and functionality
- signs, symbols, artifacts
→
a framework for understanding environment – User relationship in
service organizations
Roles
of the servicescapes
- package
- facilitator
- socializer
- differentiator
Facility Layout
- product layout/ service layout/ process layout
- every customer has different requirements. Therefore a product layout differs from a service layout, i.e. it does not work like an assembly line
- it depends on customer needs, might require employees with multiple skills to improve service → measure of effectiveness
- if its a completely new location without given figures, go to a comparably similar location
Closeness Ratings Grid
Product Layout
How
many numbers of stations are needed?
Bottle
neck, throughput time, cycle time, capacity utilization
sometimes
it might be useful to stock production part to not waist idle time or
access an inventory
combine
individual steps according to duration for most efficient outcome,
divided on stations.
Lecture VI - Service
Facility Location 29.09.11
Blueprint – discussing
the case for Laundry Service
- physical evidence needs to be made visible for customer, i.e. one individual carrying bag
- drop & leave rather than waiting in line, need sufficient counters
- “getting back to the loop”
- How to simplify my problem? “do not break down into too many points”
- Able to predict the future demand? → depends upon market segment
- Routing – does it impact the decision to be made? → Asking to give option
Service Facilitating
Location – Presentation
- demand pulled factors
- supply pulled factors
- work life balance
Selection Consideration
- access
- visibility
- traffic
- parking
- expansion …
Effect of optimization
criteria on location
- maximize utilization (e.g. Indians visiting a mall to check out the AC)
- minimize distance per capital/ person (when buying day to day items)
- minimize distance per visit
What is the targeted
market?
Single facility model and
multiple facility model
Single facility location
using cross media approach
Application of centre of
gravity method
- Euclidean metric equation
- In mathematics, the Euclidean distance or Euclidean metric is the "ordinary" distance between two points that one would measure with a ruler, and is given by the Pythagorean formula. By using this formula as distance, Euclidean space (or even any inner product space) becomes a metric space. The associated norm is called the Euclidean norm. Older literature refers to the metric as Pythagorean metric.
Qualitative
approach – factor rating method
- which location is better?
Lecture V - New service development and process design 27.09.11
Presentation
about Apollo hospital case
- Value to employee- benefits
- value cost leveraging
- “If market is wrong, whatever I do is wrong”
- supplementary service, e.g. during low season stay one night free
- matching price level of competitors
- wholly owned vs. licensing (difficult quality control) vs. HMO (expansion model)
clear
target → look up values that fit → how to deliver? Is what you
give in the end in sync with what was on paper? (fulfil claims/ match
expectancy with performance?)
What
to do? Where to put risk?
Might
learn from Hydrabad → for new project make analysis before to
select right target market
different
business expectations
- hospital – input output are people, (multi facility)
- insurance – input money, output few people as possible (multi service)
What
is a service design? Main Principles
- know your customer
- determine which of the customer's needs will be satisfied
- service strategy + position the service for competitive advantage
- minimal handoff's (Übergabe/ Weiterreichen) → customer satisfaction
- design back room operations to support front room operations
- determine the extend of customer contacts & participations
- build flexibility & robustness into system
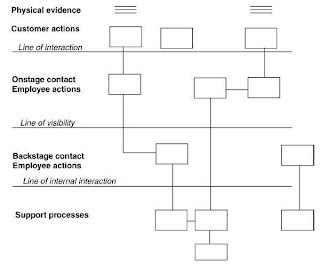
Service
Mapping/ Blueprinting (components)
- processing
- points of interaction/ contact
- backstage contact
→ might
be used to first develop/ design service on paper, then try it on a
small scale to estimate success. Then expand (e.g. Fortis hospitals
in India)
How
would I like to design my service? Building a service step by step
- helps to identify fail points/ gabs
- can be used for training of employees
- setting a quality standard (where to do decisions)
degree
of complexity
degree
of divergence (Divergenz, Abweichung) – (freedom for employee in
service performance)
“Bring
forth as much detail as it takes for decision maker to decide”
Read
article: “Designing Services that deliver” for an upgrade on the
basic blueprinting model
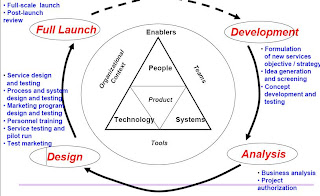
Data
Envelopment Analysis
Data envelopment analysis
(DEA) is a linear programming based technique for measuring the
relative performance of organisational units where the presence of
multiple inputs and outputs makes comparisons difficult. This
tutorial paper introduces the technique and uses an example to show
how relative efficiencies can be determined and targets for
inefficient units set. The paper also considers a number of practical
issues of concern in applying the technique.
For further reference
Lecture IV – Student Presentation 16.09.11
Use of behavioral Science
- Always a perception prior consuming a service
- → perception is reality → How can I use it for designing it? It is most important how the customer interprets the service reality
- Duration Effect
- Sequence effect > remember only parts
- Rationalization effect – customer tries to understand what he does not
Five Principles of
Customer Service
- Finish strong – most memorized ?
- Get the bad experience early out of the way, BUT bad experience NOT at first contact
- combine the Pain (limited) and segment the pleasure
- Build commitment through choice (perception of being in control of the process is desired by consumer “Prosumer”/ “Prosumption”
- Give people rituals and stick to them
How do I plan it in a
better way?
- distracting during waiting cues, television e.g.
- attract the right customer and have the right customer mix using the service → avoid confrontation
- Ergonomics (or human factors) is the scientific discipline concerned with the understanding of interactions among humans and other elements of a system, and the profession that applies theory, principles, data and methods to design in order to optimize human well-being and overall system performance. - wiki
Service Profit Chain
→ Focus on satisfied
customers → enhance their relationship → customer loyalty
Something new is required
to provoke change by breaking habits
- e.g. change of technology, human change → cause working life becomes routinised and customer's need change throughout the time!
Caste study – Apollo
Hospitals,
first corporate hospitals to start its service in India building up infrastructure
and letting it be used by doctors who reference a patient?
→ Then starting a
company to expand in franchise manner
success because India was/
is still missing top layer in medicine
Satisfaction Mirror
Customer Employee
- more repeat purchases - more familiarity with customer needs and ways of meeting them
- stronger tendency to complain errors - creator opportunity for recovery from errors
- higher customer satisfaction - higher employee satisfaction (HR develop.)
- lower costs - higher productivity
- better results - improved quality of services
Service Value Model
- time
- perceived quality
- intrinsic attributes (core and supplementary services)
- extrinsic attributes (outside service packages)
- non-monetary price (psychological costs like anxiety, fear etc. and other non-financial
- price/ monetary
other models: The cycle of
Capability – How to enhance a capability of service employee?
Service Profit Chain –
Happy employee = higher service value = increase customer
satisfaction
Service Strategy
Mission Vision
Target Market segment + service concept + operating strategy + service delivery system
positioning value
cost leveraging strategy/ system integration
→ Integrative elements/
providing guidelines
“Indian road either
humps or dumps”
“it's in pen and paper,
not yet implemented”
Casestudy Wallmarkt
Target market segments –
customer/ Employee (use of perceptual mapping) positioning
service concept - try to
tell customer what to expect! Vision needs to fulfill what has been
promised... fulfilling claims
Value Costs Leverage –
How to get productivity up? Cross training, employee satisfaction
Lot's of planning does not
guarantee that the plan is going to work out in practice.
Blackboard vs. “real
world”
Feedback Mechanism/
Integration of Maintenance systems
Why did Walkmarkt failed
to implement its system in China/ Europe?
- difference in infrastructure (going to rural area is very time consuming)
- cultural differences (local taste is different and better known by local enterprises) e.g. frozen food in China is not an option
- productivity of service personnel does not fulfill its purpose when an Indian enters Walmarkt just to spend time there, escaping the outside heat... someone telling him take this, that might be rather disturbing for him
- different motivation vs. wrong positioning
Lecture II - Major Characteristics of Services 12.September.11
Plan service on expected customer segments
Customer Participation in the Service Process
Overcoming Services Challenges
- Intangibility – use cues to make it tangible
- Inseparability – increase productivity of providers
- Variability – standardize service production and delivery/ scheduling service delivery
- perishability – match supply and demand
Process Matrix
low labor intensity: capital decision/ technological advances managing supply and demand
low interaction Service Factory Service Shop high interaction/ high
low customization customization, maintain
(marketing attention to Mass Service Professional Service quality, loyalty, fighting
physical surrounding) increases, managing that
hierarchy/ advancement
high labor intensity: hiring/ training/ employee welfare
start up of new units/ managing growth
The Service Package illustrated on a Repair Service
- Supporting Facilities – where located? (close to customer?) Size and Layout, area space for waiting, cafeteria
- facilitating goods - spare parts, tools for repair, inventory depends on requirements, items to provide the actual service
- Information - how do I use this information to help customer?
- Explicit Service - problem is being solved, e.g. the breaks are fixed
- Implicit Service - test driving/ extra service with psychological benefit, e.g. free tea/
show customer the repaired parts = additional benefit
Indian Saying “Customer” - Customer die of pain
Service Encounters
“You do not get a second chance to make first impression”
is the moment of truth → critical encounter with service
(efficiency vs. autonomy) Service Organization
Contact Personnel (perceived control) Customer
- All encounters are purposeful
- prior acquaintance is not required
- limited in scope
- task related information exchange dominates
- client and stuff roles are clearly defined
Customer Types
- economizing customer
- ethical customer
- personalizing customer
- convenience customer→ based on expectations and attitude
Lecture I – Service Operation Management 08.09.11
Session 1
- Role of Service in an Economy & Society
What is a service?
- act or need performed for customer
- --> When you can drop it on your foot, it is not a service (The Economist)
A service...
- is an activity or series of activities, more or less intangible nature
- mostly takes place in interaction between customer and service employee (but not necessarily)
- with/ without physical resources/ goods/ systems of the service provider
- with an aim to provide solution to customer problem
Impact of Service Sector
on Economy (Emphasis on Indian Economy)
Health of the country
(GDP) – employment – manufacturing sector – International Trade
- traditional activities in India that were done at home are placed outside because of changing working conditions
- double income, more women have work position
- → 10% growth constantly (question of sustainability)
Determinants of
growth in service sector
- income elasticity of demand (more money more spending)
- scope of work
- technological development
- participating of women in workforce
- urbanization
- regulatory policies
- external demand
- increase in life expectancy
The service package
- supporting facilities (physical resources)
- facilitating goods (the material consumed by the buyer or items provided for the consumer)
- information
- explicit service (essential or intrinsic features)
- implicit service (psychological benefits or extrinsic features which the consumer may sense vaguely)




